Table of Contents
Introduction
Varicose veins are a common yet often misunderstood condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Though they may appear to be a purely cosmetic concern, the reality is that it can lead to significant discomfort, pain, and more severe health complications if left untreated. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for varicose veins, delve into the latest scientific research on the topic, and provide valuable insights for those living with this condition. The journey to understanding and managing varicose veins is essential not only for physical well-being but also for mental and emotional health.
Understanding Varicose Veins
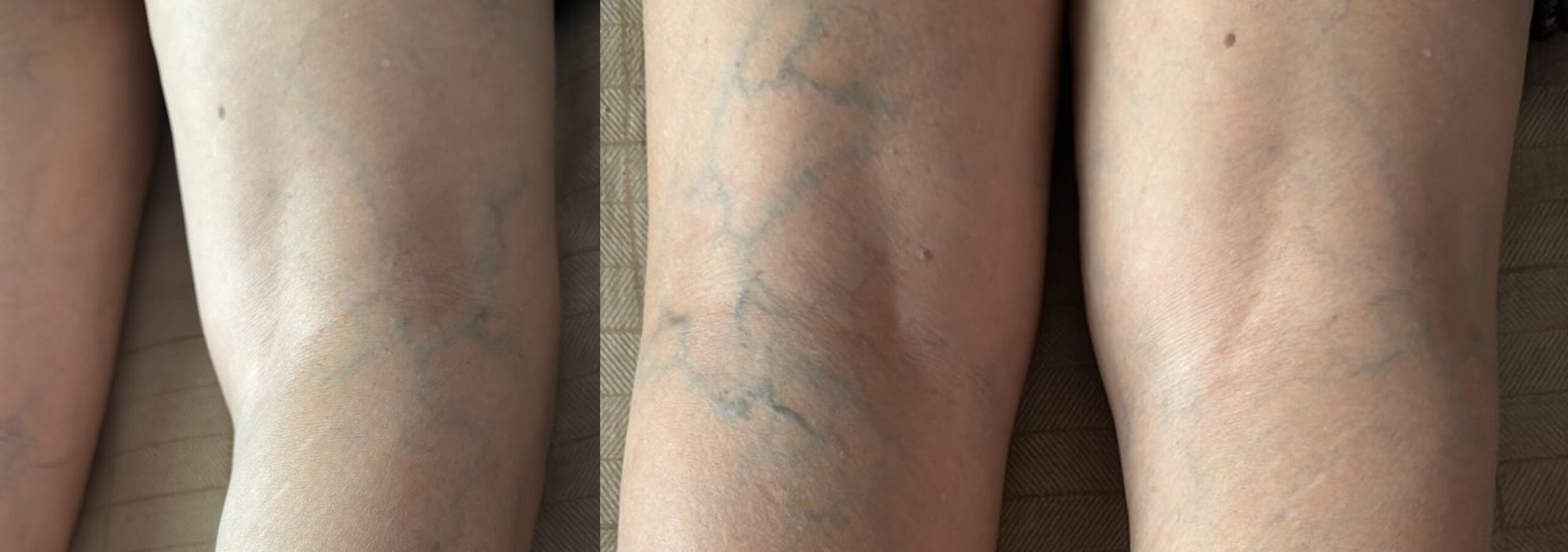
Varicose veins are a medical condition that goes far beyond the visible surface of the skin. Characterized by twisted, enlarged veins, typically appearing on the legs and feet, they are often dismissed as a minor issue. However, the discomfort and pain associated with it can impact a person’s quality of life, making it crucial to understand the underlying causes, risk factors, and effective treatments available. In this comprehensive guide, we will uncover the complexities of varicose veins, offering the latest information and actionable advice to help you or your loved ones manage this condition more effectively.
Veins are swollen, twisted veins that lie just beneath the surface of the skin. These veins most commonly occur in the legs, although they can develop in other parts of the body as well. The condition is primarily due to weak or damaged valves within the veins, which cause blood to pool and the veins to become enlarged and distorted.
While it often considered a cosmetic issue, they can cause significant discomfort, including aching, throbbing, and a heavy sensation in the legs. In more severe cases, it can lead to skin ulcers, blood clots, and chronic venous insufficiency, a condition where the veins are unable to efficiently return blood to the heart.
The Prevalence and Impact of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are a widespread condition, affecting an estimated 23% of adults in the United States alone. Women are more likely to develop varicose veins than men, with risk factors including age, family history, obesity, pregnancy, and occupations that require prolonged standing. Despite their prevalence, it often remain underdiagnosed and undertreated, leading to unnecessary suffering and complications.
The impact of it extends beyond physical symptoms. Many individuals with varicose veins experience a decline in their quality of life, due to both the discomfort caused by the condition and the emotional distress associated with the appearance of their veins. This makes it imperative to address not only the physical aspects of varicose veins but also the psychological impact they can have on a person’s well-being.
Understanding the Causes
Varicose veins develop when the valves in the veins, which are responsible for preventing the backflow of blood, become weak or damaged. When these valves fail to function properly, blood begins to pool in the veins, causing them to enlarge and become varicose. Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins.
- Genetics: A family history of varicose significantly increases the risk of developing the condition. Genetic predisposition can affect the strength and function of the vein walls and valves.
- Age: As we age, the elasticity of the veins decreases, and the valves within them may weaken, leading to an increased likelihood of varicose conditions.
- Gender: Women are more prone to developing varicose due to hormonal influences, particularly during pregnancy, menstruation, and menopause. Hormones like progesterone can cause the veins to relax, making the valves more prone to leaking.
- Pregnancy: The increased blood volume and pressure on the veins during pregnancy, along with hormonal changes, can lead to the development of varicose veins. The condition often improves after childbirth but may persist in some cases.
- Obesity: Excess body weight puts additional pressure on the veins, particularly in the legs, which can contribute to the development of varicose.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Occupations that require long periods of standing or sitting can increase the risk of it, as these positions put extra pressure on the veins and hinder proper blood flow.
- Lack of Physical Activity: A sedentary lifestyle can impair circulation and contribute to the development of varicose. Regular exercise helps to improve blood flow and reduce the risk of vein-related issues.
Symptoms and Complications
It present a range of symptoms, which can vary from mild to severe. Recognizing these symptoms early on can help in seeking timely treatment and preventing complications. Common symptoms include:
- Visible, Enlarged Veins: The most obvious symptom is the appearance of twisted, bulging veins on the surface of the skin, often blue or dark purple in color.
- Aching or Heaviness in the Legs: Many people with varicose experience a heavy or aching sensation in their legs, particularly after standing or sitting for long periods.
- Swelling: It can cause swelling in the lower legs and ankles, especially after prolonged periods of inactivity.
- Itching: The skin around veins may become dry, itchy, or irritated, sometimes leading to a rash or other skin conditions.
- Cramps or Throbbing: Some individuals experience muscle cramps, throbbing, or a burning sensation in the legs due to varicose.
- Restless Leg Syndrome: It can contribute to restless leg syndrome, a condition characterized by an uncontrollable urge to move the legs, often accompanied by uncomfortable sensations.
Complications Associated with Varicose Veins
While varicose conditions are often viewed as a minor issue, they can lead to more serious complications if left untreated:
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: This condition occurs when it impair the function of the venous system, leading to long-term issues with blood flow in the legs. Symptoms include persistent swelling, skin changes, and the development of ulcers.
- Venous Ulcers: It can cause skin ulcers, particularly around the ankles, due to the increased pressure in the veins and poor blood circulation. These ulcers can be painful and may take a long time to heal.
- Blood Clots (Thrombophlebitis): It increase the risk of developing blood clots, which can cause inflammation, pain, and swelling in the affected area. In rare cases, blood clots can travel to the lungs, leading to a life-threatening condition known as pulmonary embolism.
- Bleeding: The skin over veins of varicose is often thin and delicate, making it more susceptible to injury and bleeding. In severe cases, varicose veins may rupture, leading to significant blood loss.
Diagnosis and Treatment Options
If you suspect you have varicose, it is important to seek a professional diagnosis. A healthcare provider will typically perform a physical examination and may recommend additional tests, such as an ultrasound, to assess the severity of the condition and determine the most appropriate treatment options.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
For many individuals, non-surgical treatments can effectively manage the symptoms and prevent complications of varicose.
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings is one of the most common non-surgical treatments for it. These specially designed socks apply pressure to the legs, helping to improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
- Lifestyle Changes: Making certain lifestyle changes can help manage varicose conditions, including maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting, and elevating the legs to reduce pressure on the veins.
- Sclerotherapy: This procedure involves injecting a solution directly into the veins of varicose, causing them to collapse and eventually fade from view. Sclerotherapy is a minimally invasive treatment that can be performed in a doctor’s office with little to no downtime.
- Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT): EVLT is a minimally invasive procedure that uses laser energy to close off varicose veins. The laser is delivered through a thin fiber inserted into the vein, causing the vein to collapse and be absorbed by the body over time.
Surgical Treatment Options
In more severe cases of varicose conditions, surgical intervention may be necessary. Some of the most common surgical treatments include:
- Vein Stripping: Vein stripping is a surgical procedure in which the affected veins are removed through small incisions in the skin. This procedure is typically reserved for more severe cases that have not responded to other treatments.
- Ambulatory Phlebectomy: This procedure involves removing veins of varicose through a series of tiny incisions along the vein’s path. Ambulatory phlebectomy is usually performed under local anesthesia and allows for a quick recovery.
- Endoscopic Vein Surgery: Endoscopic vein surgery is a less common procedure that is typically used for cases of chronic venous insufficiency with skin ulcers. During the surgery, a small camera is inserted into the leg to guide the removal of the affected veins.
Recent Advances in Varicose Vein Treatment
The treatment has seen significant advancements in recent years, driven by the development of new technologies and techniques. Some of the latest innovations are listed below.
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): RFA is a minimally invasive procedure that uses radiofrequency energy to heat and close off varicose vein. This treatment is similar to endovenous laser therapy but uses a different type of energy to achieve the same results. RFA is associated with less pain and faster recovery times compared to traditional surgery.
- VenaSeal Closure System: The VenaSeal Closure System is a newer treatment option that uses a medical adhesive to close off varicose vein. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia and does not require the use of compression stockings after treatment. The VenaSeal system offers a quick recovery and minimal discomfort for patients.
- Mechanochemical Ablation (MOCA): MOCA is a novel treatment that combines mechanical disruption of the vein with the delivery of a sclerosing agent. This approach is designed to enhance the effectiveness of sclerotherapy and improve patient outcomes. MOCA is a relatively new treatment and is still being studied for its long-term efficacy.
Managing Varicose Veins: Practical Tips and Advice
Living with varicose veins can be challenging, but there are several steps you can take to manage the condition and improve your quality of life. Here are some practical tips and advice for managing varicose veins:
- Stay Active: Regular exercise is one of the best ways to improve circulation and reduce the risk of varicose veins. Activities like walking, swimming, and cycling are particularly beneficial for promoting healthy blood flow in the legs.
- Elevate Your Legs: Elevating your legs above the level of your heart for 15 to 20 minutes a few times a day can help reduce swelling and relieve discomfort associated with varicose veins.
- Wear Compression Stockings: If you have varicose veins, wearing compression stockings can help prevent the condition from worsening. Compression stockings are available in different strengths and can be prescribed by a healthcare provider based on your specific needs.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body weight can put added pressure on your veins, making varicose veins more likely to develop or worsen. Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise can help alleviate this pressure.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting or Standing: If your job requires long periods of sitting or standing, try to take breaks every hour to move around and stretch your legs. This can help improve circulation and reduce the strain on your veins.
- Consider Dietary Changes: A diet high in fiber and low in salt can help prevent constipation and reduce swelling, both of which can contribute to the development of varicose veins. Incorporating more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains into your diet can promote better vein health.
Mental and Emotional Impact of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins are not just a physical condition; they can also have a significant impact on mental and emotional well-being. The visible nature of varicose veins can lead to feelings of self-consciousness, embarrassment, and even depression. Many individuals with varicose veins may avoid wearing certain types of clothing, such as shorts or skirts, and may refrain from activities that expose their legs.
The emotional burden of varicose veins can be particularly challenging for those who are already dealing with chronic pain or discomfort. It is important to address these feelings and seek support from healthcare providers, therapists, or support groups if needed. Building a support network can help individuals with varicose veins cope with the emotional challenges of the condition and find strategies to improve their self-esteem and quality of life.
Conclusion
Varicose veins are a common yet complex condition that affects millions of people around the world. While they are often viewed as a cosmetic concern, the reality is that varicose veins can cause significant discomfort, pain, and even lead to more serious health complications. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for varicose veins is essential for managing the condition effectively.
Recent advances in medical technology have made it easier than ever to treat varicose veins, with a range of minimally invasive options available. However, prevention and early intervention are key to minimizing the impact of varicose veins on your life. By staying active, maintaining a healthy weight, and seeking timely medical care, you can reduce your risk of developing varicose veins and manage the condition if it does occur.
Remember, varicose veins are not just a surface-level issue—they can have a profound impact on your physical, mental, and emotional well-being. If you are struggling with varicose veins, do not hesitate to reach out to a healthcare provider for guidance and support. With the right care and treatment, you can alleviate the pain and discomfort associated with varicose veins and improve your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What are varicose veins? Varicose veins are swollen, twisted veins that lie just beneath the surface of the skin, usually occurring in the legs.
- Are varicose veins dangerous? While varicose veins are generally not life-threatening, they can lead to complications such as ulcers, blood clots, and chronic venous insufficiency if left untreated.
- What causes varicose veins? Varicose veins are caused by weak or damaged valves in the veins, which allow blood to pool and the veins to enlarge.
- Can varicose veins be treated without surgery? Yes, there are several non-surgical treatments available for varicose veins, including compression stockings, sclerotherapy, and laser therapy.
- Do varicose veins go away on their own? Varicose veins do not go away on their own and may worsen over time. However, treatment can help alleviate symptoms and prevent complications.
- Is it possible to prevent varicose veins? While you may not be able to prevent varicose veins entirely, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, exercising regularly, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing can reduce your risk.
- Can men develop varicose veins? Yes, men can develop varicose veins, although they are more common in women.
- What is the latest treatment for varicose veins? Some of the latest treatments for varicose veins include radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and the VenaSeal Closure System, both of which are minimally invasive procedures.
References
https://www.jvascsurg.org/article/S0741-5214(11)00327-2/fulltext
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK556120
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5731590
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/25/3/1560
https://www.mdpi.com/2227-9032/11/24/3183
https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/13/9/2539
https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/10/15/3239
YouTube video linkhttps://youtube.com/shorts/DxcLvxvhCug